Causes Of Alveolar Bone Resorption</2>
Periodontal Disease
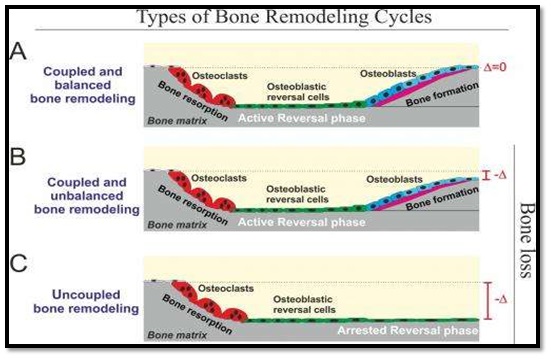
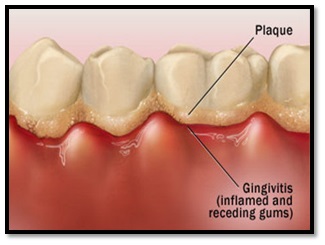
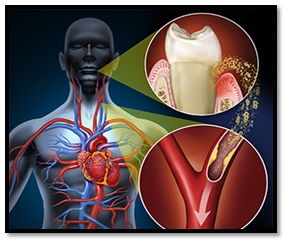
Periodontal disease is a chronic disease of the soft and hard tissues supporting the teeth and is caused by oral bacteria resulting in plaque and bacterial aggregation inside the gums leading to gums inflammation and loss of alveolar bone slowly and gradually and finally tooth loss in severe cases.
Bacterial plaque, a colorless membrane forms on the surface of the teeth and is the most common cause of periodontal diseases. Although periodontal disease can be treated to an extent, the bone loss is irreversible. It also increases the risk of stroke, heart attack and other health issues but most cases of periodontal diseases are preventable through good and proper oral hygiene.
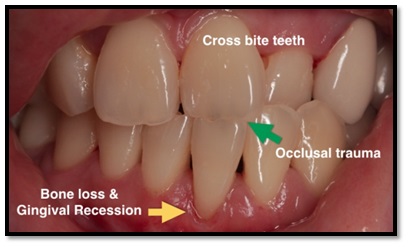
Trauma from occlusion (TFO)
Trauma from occlusion is the persistent trauma of the teeth due to occlusion resulting in widening of the periodontal ligaments and occurs with or without the presence of inflammation. In absence of inflammation, the changes that occur are reversible and cause angular shape bone loss but when it occurs along with inflammation, it increases the level of bone destruction and causes bizarre pattern of bone loss.
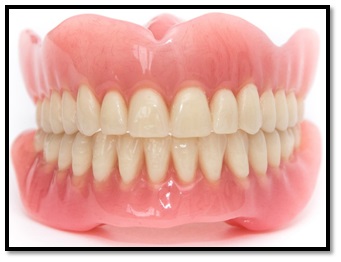
Removable Prosthesis
The use of removable prosthesis for a long time results in abrasion and erosion of the underlying alveolar bone on which the denture rests, thereby gradually destroying it and impeding the placement of the fixed teeth. Hence, patients with removable prosthesis are advised to undergo regular dental check ups.
Treatment
Proper oral hygiene is to be maintained even if the teeth and gums are healthy. With recent advances in dentistry fixed teeth can be placed even in resorbed ridges with minimally invasive techniques like zygomatic implants, angled implants, pterygoid implants or bone grafts, etc and are highly effective in restoring the beautiful teeth and smile.

Proper oral care involve brushing the teeth twice daily, regular flossing, use of mouthwash for extra protection, etc. Deep cleaning of the gums and below gumline, is done to eliminate the bacteria and help in regeneration of the lost alveolar bone. For severe cases where non-surgical treatments are not effective, surgical management like flap surgery, bone graft, etc may be required.
Flap surgery is done to remove deep pocket’s, plaque and calculus. The gums are then pulled back and sutured to fit closely to the tooth and left to heal.
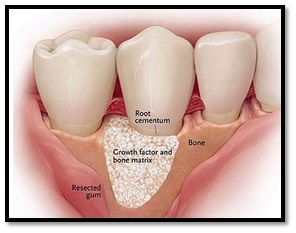
Bone grafts also help in regenerating the resorbed alveolar bone by placing natural or synthetic new bone thereby restoring the bone volume and height.
Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) is a surgical procedure that uses a barrier membrane placed between the gum and the bone to regenerate and repair both the hard and soft tissues by stopping the gums from growing into the bone space.
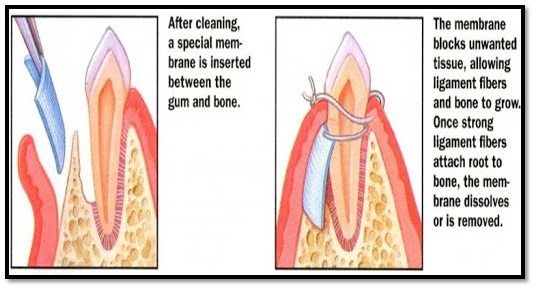
Besides, diets rich in calcium and vitamin D can also reduce the amount of bone loss and the prognosis depends on the oral hygiene, stage of the disease, habits like smoking, etc.