Bone has the ability to regenerate by itself. Bone graft is the material used in bone grafting. Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces resorbed bone or areas which have failed to heal properly, that may pose a significant health risk to the individual.
The principles involved in bone grafting are:-
Osteoconduction – it is a process where the bone graft material serves as a scaffold for new bone formation and guides the growth of the natural bone.
Osteoinduction – it is the process of stimulation of progenitor cells to become active osteoblasts. The BMP (bone morphogenic proteins) is the most common osteoinductive cell mediators.
Osteogenesis – it is the process in which bone cells present in the graft material contribute to bone remodeling. It occurs only in autogenous bone graft and allograft cellular bone matrices.
The bone graft can be in the form of blocks, granules, powder or putty that can be injected with the help of syringe. Most bone grafts are expected to be reabsorbed and replaced as the natural bone heals with time.
Bone graft can further be classified as –
- Autograft (patient’s own bone)
- Allograft (cadaver bone)
- Alloplastic graft
- Xenograft
Autograft
Bone graft harvested from the same individual receiving the graft. The most common site for graft is iliac crest, chin region (symphysis), ramus region, etc. It is also the most preferred bone graft due to its osteoconductive, osteoinductive and osteogenic properties and there is very less risk of graft rejection. The only drawback is the second surgery site.
Allograft
They are bone grafts which are harvested from different individual but from the same species. They are obtained from cadaver which are stored in bone banks for future use. Fresh frozen bone, Freeze dried bone allograft (FDBA), Demineralized freeze dried bone allograft (DFDBA) are types of allografts.

Alloplastic grafts
They are synthetic bone grafts which are obtain from hydroxyapatite crystals. It has osteoconductive, hardness and acceptability properties. Marine algae coralline officinalis has fluorohydroxyapatite as composition, which is similar to human bone and is also considered as a standard alloplastic material.

Xenograft
Bone grafts obtained from a donor of a different species like bovine bone which are obtain as a calcified matrix and can be freeze dried or demineralized and deproteinised. Coral based xenografts obtain from madrepore or millepore corals mainly contain calcium carbonate and gives coral derived granules and other types of coralline xenografts.
Uses of Bone Graft in Dentistry
Periodontally compromise teeth
In periodontally compromise teeth, the teeth may become mobile due to bone resorption so grafting is required to regenerate the surrounding bone and support the teeth.
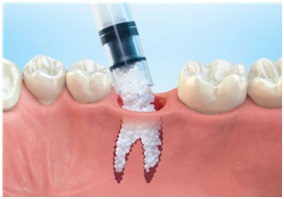
Socket preservation or Ridge preservation
It is done to maintain the socket after tooth extraction. Usually after tooth extraction, the jaw bone has a natural tendency to lose its original shape and 30-60% of bone resorption occurs in the first 6 months. To prevent this and for wound care bone graft placement is done in the socket after extraction. The graft will act as a scaffold for new bone formation and will reduce the rate of bone resorption. Also, to maintain ridge volume and prevent ridge atrophy.
Bone defects
Placement of bone graft in bone defects due to trauma or infections.
Dental implants
One of the most important factors to be considered in the success of implant treatment is the quality and quantity of bone. A good volume of bone is needed for better stability of implants. So bone grafting needs to be done whenever necessary.
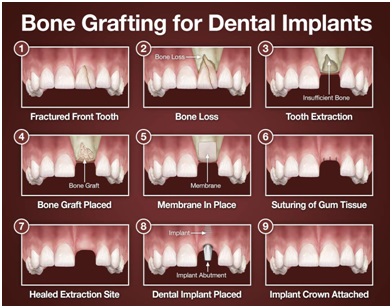
Bone grafting promotes bone healing and growth. Some other specific reasons for bone graft are:
A fracture that won’t heal without a graft.
Bone diseases like osteonecrosis or cancer.